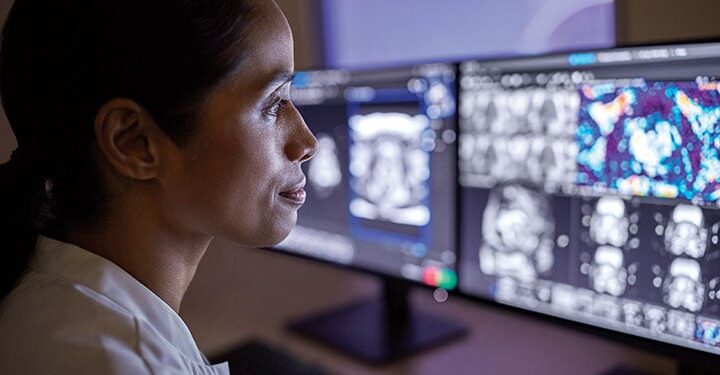
Radiology is the study of imaging using X-rays and other types of radiation. AI has the potential to transform this field by automating routine tasks and increasing the accuracy of radiologists.
AI can assist radiologists with reading medical images by eliminating redundancies in their work and providing relevant information that they might not have considered. For example, AI can interpret signals from CT scans to spot unexpected growths or artefacts in an image that a radiologist might otherwise miss.
To help radiologists process CT scans more efficiently, digital radiology vendor Panorama sleuths through several free resources on the internet and identifies some useful tips and tricks that you might find helpful when working with digital radiology software.
What is digital radiology?
Digital radiology is the technology that allows images to be stored, analyzed, and interpreted from a computer. Digital radiology encompasses a wide range of applications, from X-ray imaging for medical diagnosis to cybersecurity surveillance. There are more than 100 million CT scans taken every year in the United States.
This number is expected to increase as the population ages and a greater number of people seek medical imaging. The ability to quickly and efficiently process large volumes of CT scans is critical for radiologists to efficiently interpret images.
How does AI help radiologists with CT scans?
The technologies used to create CT images can create signals that indicate structures in the image, but they don’t necessarily translate into visible signs in the image. For example, white blood cells in a CT scan might be large enough to appear as a growth on the scan.
AI can be used to identify these hidden abnormalities and provide useful information to radiologists. AI can also be used to automate tasks that are repetitive and slow. For example, it can create a CT dataset of images to create a baseline for future scans to ensure that reading is as efficient as possible.
AI can also be used to detect additional findings that might otherwise go unnoticed by radiologists. For example, AI can spot unexpected artefacts in an image that a radiologist might otherwise miss.
Benefits of AI and why you should use it in clinical practice
Transforming the daily workflow for radiologists is a major goal for many AI startups. Decreased time spent on the task and increased accuracy in the reading process can translate into fewer errors and improved patient care. New workflows and tools can also decrease the risk of human error in laboratory work and other settings.
In addition, AI can help radiologists stay more productive and avoid the stress that can negatively affect their performance. This can be particularly important for doctors who spend long hours in the clinic or imaging suite.
Radiologists who adopt AI can also increase their income by automating tasks that once required a full-time human presence. AI can be particularly helpful if you work long hours or have irregular schedules.
Set up a data pipeline to identify images for AI processing
If you’re using digital radiology software that supports AI, it can automatically identify images that need to be scanned or reviewed by a radiologist. The best way to set up this pipeline is with a continuous imaging system (CIS).
A CIS can be programmed to detect abnormalities in a patient’s CT scan and prompt radiologists to review the scan in real time. This can be particularly helpful for scanning patients who are unconscious or unable to communicate.
Train algorithms on a dataset of relevant images
The work that AI does to help radiologists with CT scans can be summarized in a set of rules or algorithms. AI, that’s been trained to read CT scans can then be used to process images.
Training an AI on a dataset of images can take a few different approaches. The first is to create a set of images that have been annotated with labels. Annotating images can allow radiologists to provide labels such as “car,” “tree,” or “brain tumour.”
Use the algorithm to improve CT reading efficiency
Once AI has been trained to identify CT scans and flags them for review by a radiologist, you can use the algorithm to improve reading efficiency. For example, AI can flag images that need to be reviewed by a radiologist if there’s an unexpected finding in the scan.
AI can also flag an entire series of images that need to be reviewed by a radiologist for a particular reason such as a tumour. When reading images by a human, these flags and annotations can speed up the process and help to ensure that no important findings are missed and that the entire scan is reviewed.
Make sure that all identified CT readings are reviewed by a radiologist
Once the AI has been trained to identify CT scans, it can be used to process images. This can help to increase the accuracy of the scans as well as improve the speed of reading.
However, AI should not be used to make decisions on its own. The AI should only be used to flag scans for review based on the annotations and rules it’s been trained on.
When an AI has been used to flag a scan for review, the radiologist should review the image. This can ensure that the reading is accurate and that the entire scan isn’t missed.
Conclusion
If your practice uses digital radiology software, you can use AI to find and flag images that need to be reviewed by a radiologist and speed up reading. AI can also help to improve the accuracy of your scans and speed up reading by flagging scans that need to be reviewed.
These benefits of AI can help radiologists to stay productive and reduce the risk of stress. Now that you know more about AI in radiology, you’ll see how it can transform the work of radiologists with CT scans.